Microservice application built using Flask and deployed on Kubernetes. It is designed to demonstrate how to build and deploy microservices on a Kubernetes cluster
Kubeadm Installation Guide
This guide outlines the steps needed to set up a Kubernetes cluster using kubeadm.
Pre-requisites
Ubuntu OS (Xenial or later)
sudo privileges
Internet access
t2.medium instance type or higher
Both Master & Worker Node
Run the following commands on both the master and worker nodes to prepare them for kubeadm.
# disable swap
sudo swapoff -a
# Create the .conf file to load the modules at bootup
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/modules-load.d/k8s.conf
overlay
br_netfilter
EOF
sudo modprobe overlay
sudo modprobe br_netfilter
# sysctl params required by setup, params persist across reboots
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
EOF
# Apply sysctl params without reboot
sudo sysctl --system
## Install CRIO Runtime
sudo apt-get update -y
sudo apt-get install -y software-properties-common curl apt-transport-https ca-certificates gpg
sudo curl -fsSL https://pkgs.k8s.io/addons:/cri-o:/prerelease:/main/deb/Release.key | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/cri-o-apt-keyring.gpg
echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/cri-o-apt-keyring.gpg] https://pkgs.k8s.io/addons:/cri-o:/prerelease:/main/deb/ /" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/cri-o.list
sudo apt-get update -y
sudo apt-get install -y cri-o
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable crio --now
sudo systemctl start crio.service
echo "CRI runtime installed successfully"
# Add Kubernetes APT repository and install required packages
curl -fsSL https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.29/deb/Release.key | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg
echo 'deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg] https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.29/deb/ /' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
sudo apt-get update -y
sudo apt-get install -y kubelet="1.29.0-*" kubectl="1.29.0-*" kubeadm="1.29.0-*"
sudo apt-get update -y
sudo apt-get install -y jq
sudo systemctl enable --now kubelet
sudo systemctl start kubelet
Master Node
Initialize the Kubernetes master node
```bash sudo kubeadm config images pull
sudo kubeadm init
mkdir -p "$HOME"/.kube sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf "$HOME"/.kube/config sudo chown "$(id -u)":"$(id -g)" "$HOME"/.kube/config
Network Plugin = calico
kubectl apply -f raw.githubusercontent.com/projectcalico/cal..
kubeadm token create --print-join-command
**<mark>Expose port 6443 in the Security group for the Worker to connect to Master Node</mark>**
* ## Worker Node
* Run the following commands on the worker node.
* ```bash
sudo kubeadm reset pre-flight checks
sudo your-token --v=5
Paste the join command you got from the master node and append --v=5 at the end. Make sure either you are working as sudo user or usesudo before the command.
Deployment of a Microservices Application on K8s
- Do Mongo Db Deployment
- Do Flask App Deployment
- Connect both using Service Discovery
Installation
To install and run the application on your Kubernetes cluster, follow these steps:
Clone this repository to your local machine.
git clonehttps://github.com/SanketShirke/Microservices-K8s.gitNavigate to the project root directory.
Create a Kubernetes deployment and service by running the following command:
kubectl apply -f <yml files.yml

Verify that the deployment and service have been created successfully by running the following command:
kubectl get nodes
kubectl get pods
kubectl get deployments
kubectl get services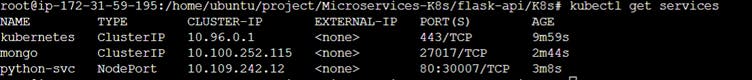
After that go to your AWS account click on master node go to security group and create a port number as per your given in python-svc.yml
Example:-
http://ip.adress:30007After that open a new tab and past your
IPandport number
If everything is working properly, you should see the name of your deployment and service listed in the output.

